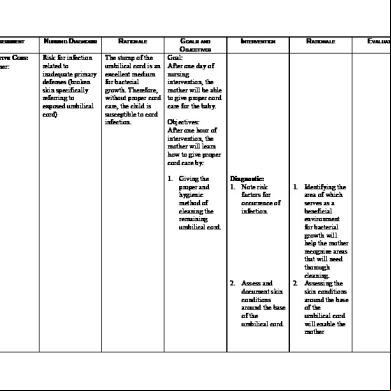
Care Plan 735h6i
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3i3n4
Overview 26281t
& View Care Plan as PDF for free.
More details 6y5l6z
- Words: 3,798
- Pages: 11
BASIC CONDITIONING FACTORS:-.5 Client Initials: _J.K. Sex: __M Age:_32 Race: White Allergies: Pamelor, Zomig, Skelaxin ________________________________________________________________________________ Medical Diagnosis: Left Shoulder and Arm Pain ______________________________________________________________________________ Surgical Procedure / Treatment: Left Shoulder Arthroscopy Bicep Tenodoesis Subacromial Bursectomy Removal Foreign Body__________________________________________________________________________________ Client Profile: (reason for hospitalization, chief complaints and/or presenting symptoms) Patient presenting for preoperative evaluation for left shoulder arthroscopy, Bicep Tenodesis, Subacromial Bursectomy, and Removal of foreign body. Patient injured arm/shoulder about one year or more ago at work. Patient complains of pain in left shoulder area. ____________________________________________________________________________ Past Medical/Surgical History of Client(including previous hospitalizations with dates) Patient injured his arm about 1year ago at work. Has undergone two surgeries and pt. continues to complain of pain. Labrum repair left shoulder 11/09, Ulnar transposition left elbow 09/09 Patient also experienced seizures as a child but has not experienced any in many years. Patient has history of asthma but has not needed to use his inhaler and cannot the last time he needed the use for it. Pt. has back pain and has had a facet rhizotomy injection Pt. also does have anxiety and palpitations. Palpitations are controlled with atenolol and panic is controlled with clonazepam. Family History (include three tier genetic history): Mother: Died at the age of 88 had breast and bladder cancer Father: Died at the age of 72 had cancer of the larynx Sister: Age 29 Hyperthyroidism Married daughter 2yrs son 5yrs Sister: Age 25 Married___________________________________________________________________________ Systems: (family, friends, coworkers etc.) Wife, Two children (boys 9yr, 1yr), Coworkers, Neighbors, Friends, Family _______________________________________________________________________________ Sociocultural and daily patterns of living: Pt. lives in a home with his two children and wife. Pt. son also has asthma. His activities consist of work as a local truck driver and when he comes home he likes to spend time with kids and family. He is a non-practicing catholic.
POWER COMPONENTS: _A__ Attention Span (Acute Limited attention span due to anesthesia) _A_ Energy Level (Acute decrease in energy level due to anesthesia) _A__ Control of body movements (Acute control loss due to anesthesia) _A__ Ability to reason (Acute ineffective ability to reason due to anesthesia) _A__ Ability to make decisions (Acute inability to make decisions due to anesthesia) _A__ Motivation (Acute deficit in motivation due to anesthesia) _A__ Knowledge of health problem (Patients knowledge deficit in removal of foreign body and where it came from is diminished) _A__ Ability to provide for self care (Acute inability to provide for self-care due to anesthesia and surgical incision) _A__ Skills needed to adapt self-care needs (Patient will difficulty with adapting to self care needs without the assistance of left arm while recovering) _A__ Ability to adapt self-care needs to A.D.L. (Patient will have difficulty with A.D.L.’s due to limited extremity movement.)
UNIVERSAL / HEALTH DEVIATION SELF-CARE REQUISITE ASSESSMENT: Air (Respiratory, Cardiovascular)-3 Preop: Bp: 109/73, Temp: 98.2, Apical Pulse: 64, regular and strong, Normal EKG, Respirations: 18, Easy on room air. Lung sounds: Bilaterally equal, No secretions, SaO2:98%, Capillary refill: <2 sec. Heart sounds: normal. Pt does not complain of chest pain but does state that he does have hypertension. Mucous membrane: moist, Nail bed color: Pink. Serum Lab results: Glucose: 85 Creatinine: 1.0 Serum Calcium: 9.7 Total bilirubin: 0.2 Alanine Aminotransfer: 32 AST: 16 Alkaline Phosphatase: 63 Chloride: 101 Carbon Dioxide: 28 Granulocyte percentage: 5.3 Granulocyte Absolute: 5.3 Lymph Percent: 26.5 Lymphocyte Absolute: 2.2 Monocyte Percent: 8.3 Monocyte Absolute: 0.7 Eosinophil Percent: 1.4 Eosinophil Absolute: 0.1 Basophil Percent: 0.2 Basophil Absolute: .0 WBC: 8.4 RBC: 4.71 Hemoglobin: 14.5 Hematocrit: 42.4 MCV: 90 MCH: 30.8 MCHC: 34.2 Platelets: 220 RDW: 13.2 PT: 10.3 PTT: 27.9 Pt. had chest x-ray done: Frontal and lateral projections of the chest demonstrate biapical pleural parenchymal scarring. Lung volumes show large but otherwise clear. Heart size within normal limits. Postop: Bp: 115/62 Apical pulse: 66 SaO2: 94% on room air, Lung sounds bilaterally equal. Resp:16 Radial pulse strong.. Warm temperature normal color of extremities. Sensation: numbness in left arm due to interscalene block. Extremities normal color, cap <2, no edema present. Water (Renal, F & E) Urine Clear yellow. Urinanalysis: Ph: 7.0 Specific Gravity: 1.003 Glucose: Negative Blood: Negative Ketones: Negative Protein: Negative Urobilinogen: <2.0mg Bilirubin: Negative Leukocyte Esterase: Negative Nitrate: Negative GFR: >=60 Sodium: 139 Potassium: 4.6 Total Protein: 7.9 Albumin: 4.6. Preop:1000ml IV Lactated Ringers, NPO Food / Elimination (Gastrointestinal) Abdomen soft, no masses,. Bowel sounds present in all four quadrants. Patient has crowns. No guarding or rebound. Skin turgor normal. Oropharynx pink and moist. Postop: pt ate 4 oreo cookies and had 3sips of pepsi. Activity & Rest (Musculoskeletal, Neurological) Pt. has limited ROM due to surgery, sleep patterns normal. Sensory and motor intact, PERRLA, pt. has pain and limited movement in L. arm due to Surgery. Pt. also complains of previous back pain for several months. Pt. denies sleep, anxiety, depression problems. Solitude & Social Interaction (Sensory Perception, Psychosocial) Pt. does not wear glasses. Interaction with family and friends is close and normal. No issues in communication. Pt. does not use antidepressants or anti-seizure medication. Prevention of Hazards (Endocrine Autoimmune, Chemical) Pt. smokes 1pack in two weeks. Alcohol consumption: 6pk in month, Seizures as child no longer has episodes. Home environment safe. Anesthesia istered during surgery: Versed, Fentanyl, Lidocain. Foreign body removed during surgery. Side rails up during transport. Dressings clean. Incision made at left anterior shoulder. No drainage noticed post operation. Promotion of Normalcy (Personal Hygiene, Self Concept, Reproductive, Integument) Preop: Skin intact no lesions. IV right anterior forearm Postop: patient had a Cuff IC and was unable to move arm. Pt had incision on left shoulder no drainage present. Patient confirmed of no anxiety feeling day of surgery. No anxiety was seen in facial expressions. Pain after surgery was at 0 (1-10 scale). Patient is able to complete ADL with assistance due to surgery.
DEVELOPMENTAL SELF CARE REQUISITES: Client’s Age: 32 Stage of Development: Generativity Vs. Self Absorption How might this illness interfere with the client’s developmental tasks: How might the client’s stage of development impact his/her adjustment to the illness? Erikson observed that middleage is when we tend to be occupied with creative and meaningful work issues surrounding out family. The significant task is to contribute to the betterment of society, which for the patient is now not able to do. The patient has to focus on himself to further increase his health and to provide an adequate amount of time for his surgery incisions to heal. This stage of development may impact the patient very easily. The patient is an eager and willing man and would to anything for his family, even if it did include not letting his shoulder rest after the surgery; prolonging the healing time.
Research of the Medical Diagnosis Arthroscopic Bicep Tenodesis: Arthroscopy is a procedure that allows direct visualization of a to diagnose t disorders. Treatment of tears, defects, and disease processes may be performed through the arthroscope. The procedure is performed through the arthroscope in an operating room, under sterile conditions. Injection of a local anesthetic agent into the t or general anesthesia is used. A large bore needle is inserted and the t is tended with saline. The arthroscope is introduced and t structures, synocium, and articular surfaces are visualized. After the procedure the puncture wound is closed with adhesive strips or sutures and covered with a sterile dressing. Complications are rare but may include infection, hemarthrosis, neurocascular compromise, thrombophlebitis, stiffness, effusion, adhesion, and delayed wound healing. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Bicept tendoesis: A biceps tenodesis is a procedure that cuts the normal attachment of the biceps tendon on the shoulder socket and reattaches the tendon to the bone of the humerus. By performing a biceps tenodesis, the pressure of the biceps attachment is taken off the cartilage rim of the shoulder socket (the labrum), and a portion of the biceps tendon can be surgically removed. Essentially a biceps tenodesis moves the attachment of the biceps tendon to a position that is out of the way of the shoulder t. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Nursing interventions: After the procedure, the t is wrapped with a compression dressing to control welling. In addition ice may be applied to control edema and enhance comfort. Frequently, the t is kept extended and elevated to reduce swelling. It is important to monitor and document the neurovascular status. Analgesic agents are istered as needed. The patient is instructed about activities and exercises that may be preformed. The patient and family are informed of symptoms to watch for in order to determine whether complications are occurring and of the importance of notifying the physician of this observation. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Subacromial Bursectomy: is removal of the subscromial bursa sac (a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion at a pressure point in the body. near ts where tendons or muscles cross either bone or other muscles). (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010)
Significance of Normal/Abnormal Diagnostic Tests Lab work: all levels are normal Urinanalysis: all levels are normal Chest X-ray: Frontal and lateral projections of the chest demonstrate biapical pleural parenchymal scarring. Lung volumes show large but otherwise clear. Heart size within normal limits. Medical Technologies: Treatments / Medications Clonazepan: 0.5mg, PRN Action: Depresses nerve impulse transmission in motor cortex. Rationale: Patient has anxiety with palpitations. Side effects: drowsiness, behavioral disturbances Nursing implications: assess for calm facial expression and decreased restlessness, assess vital signs. Atenolol: 25mg daily Action: Blocks beta-adrenergic receptors in cardiac tissue Rationale: Treatment of hypertension. Side Effects: Hypotension, dizziness, constipation Nursing Implications: Monitor B/P and pulse for bradycardia, and respirations for difficulty in breathing. Albuterol: 2 puffs q4 hrs PRN Action: Broncho dilator. Rationale: Patient has asthma but has not needed medication, and cannot the last time he has taken medication. Nursing Implications: Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations. Assess lungs for abnormal lung sounds.
Fluticasone Propionate: 2 puffs BID Action: Prevents and controls inflammation. Rationale: Patient has asthma but has not needed medication, and cannot last time he has taken medication. Nursing Implications: Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations. Assess lungs for abnormal lung sounds. Post OP ORDERS: Morphine: 2-4 mg every 2min IV PRN max dose: 20mg Action: binds with opioid receptors within CNS Rationale: Pain relief Nursing Implications: monitor vital signs 5-10 min after IV check for adequate voiding. Assess for clinical improvement. Fentanyl: 25-50 mcg every 2min IV PRN max dose: 100mcg Action: reducing stimuli from sensory nerve endings, inhibits ascending pain pathways Rationale: Pain relief Nursing Implications: Asst with ambulation, encourage post op turn, cough deep breathe q2h. Monitor Vital signs, assess for relief of pain Prochlorperazine: 10mg IM Action: Acts to block dopamine receptors in chemoreceptor trigger zone. Rationale: Relieves nausea/vomiting Nursing Implications: Monitor BP for hypotension. Monitor WBC count. Assess for therapeutic response. Onsansteron: 4mg IV Action: blocks serotonin, both peripherally on vagal nerve terminals, centrally in chemoreceptor trigger zone. Rationale: Relieves nausea/vomiting Nursing Implications: Assess for dehydration, assess bowel sounds for peristalsis, and assess mental status Meperidine: 12.5 IVP May repeat x1 Action: Binds to opoid receptors with in CNS Rationale: for shivering Nursing Implications: Monitor vitals 15-30 mins after subQ/IM dose, 5-10 mins after IV dose. Monitor pain level, bowel activity. Prioritized List of Nursing Diagnoses (in PES format Acute pain r/t injury in surgical care AEB pt. verbalization. Self-Care Deficit related to impaired ability to perform self-care tasks, as evidenced by statements of need for assistance and observed difficulty in performing activities of daily living Risk for infection r/t invasive procedure. Acute pain r/t presence of intubation tube AEB pt. verbalizing a mild sore throat. Acute back pain related to back injury as evidenced by patient verbalization. Ineffective health maintenance r/t lack of knowledge regarding prevention of dental disease AEB pt crowns. Risk for constipation r/t use anesthesia, decrease in fluid and food intake, and pain medication. Risk for ineffective breathing pattern r/t effects of narcotics and anesthesia. Risk for Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunction related to tissue trauma and Readiness for enhanced Therapeutic regimen management: expresses desire to learn measures to stop smoking.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS (NANDA)
Acute pain r/t injury in surgical care AEB pt. verbalization.
SELF-CARE AGENCY-1 Goal (NOC) + Expected Outcomes (NOC Indicators) NOC: Pt. will have a reduction in pain by discharge. NOC Indicators: Pt. will verbalize pain at a level of 3 or less by the 10/28.
NOt. knows an easier method for dressing . NOC Indicators: Pt. will verbalize three types of clothing that are easier to put on by 10/28.
Self-Care Deficit related to impaired ability to perform self-care tasks, as evidenced by statements of need for assistance and observed difficulty in performing activities of daily living Ok so you would Use selfcare deficit: dressing
Risk for infection r/t invasive procedure.
NOCindicator: Pt. will demonstrate the ability to dress. NOC Indicator: Pt. will know to dress the affected side first by 10/28.
Goal: Prevention of infection These are all indicators NOC: Pt. will know signs and symptoms of infection. NOC Indicator: Pt. will verbalize $ signs and symptoms of infection. NOC: Pt. will have surgical area that shows evidence of healing.at f/u visit
NURSE AGENCY (NIC) Nursing actions (NIC Activities) (Include rationales, Independent or Interdependent and S/E, PC, or WC) Assure patient attentive analgesic care: Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain, to include location, characteristics, onset/ duration, frequency, quality, intensity or severity of pain and precipitating factors. (Rationale: initial assessment and documentation provide direction for the pain treatment plan. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 604) Ask the client to describe past experiences with pain and the effectiveness of methods used to manage pain, including experiences with side effects, typical coping responses, and the way the client expresses pain. (Rationale: many patients harbor fears and misconceptions regarding the use of analgesics, management of side effects, and risk of addiction. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 606) Assess and document the intensity of the pain and discomfort after surgery. (Rationale: The clients report of pain is the single most reliable indicator of pain. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig [g 605) Obtain a prescription to ister and opioid. Rationale: opioid analgesics are indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain Interdependent PWC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 607) ister opioids orally or IV as ordered when appropriate and available. (Rationale: the least invasive route of istration capable of providing adequate pain control is recommended. Independent PC )(Ackley and Ladwig pg 608) When opioids are istered, assess pain intensity, sedation, and respiratory status at regular intervals. (Rationale: Opioids may cause
EVALUATION AND/OR MODIFICATIONS
Patient had reached goal, by the time of discharge patient confirmed a level of 2 out of 10 on the pain scale. Patient also verbalized the importance of not waiting till the pain was intolerable before taking the medication. Patient had reached goal: patient verbalized three easier steps of dressing that are easier to put on. (Wide sleeve shirts, sweaters that zip up in front, and dressing the affected arm first.) Patient had reached goal and indicated 5 signs and symptoms of infection. (Pain, Redness, Heat, Fever)purulentdrainage? Patient had reached goal, by the time of discharge patient did not show any signs of redness or swelling in the surgical area. Patient had reached goal. Patient verbalized the steps in correct hand hygiene, indicated the when time of surgical dressing had to be changed, and indicated to whomever was doing the dressing change required to wear gloves.
NOC Indicators: Pt. will have no redness and drainage by 10/30 and none at f/u visit NOC: Pt. will know how to change dressing. NOC Indicators: Patients will wash hands, wear gloves and apply
clean band aids to sutures.
respiratory depression because they reduce the responsiveness of carbon dioxide chemoreceptors located in the respiratory centers of the brain. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 609) Teach and implement non-pharmacological interventions when pain is relatively well controlled with pharmacological interventions. (Rationale: non-pharmacological interventions should be used to supplement, not replace, pharmacological interventions Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 609) Reinforce the importance of taking pain medications to keep pain under control. (Rationale: teaching clients to stay on top of their pain and prevent it from getting out of control improves the ability to accomplish the goals of recovery. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 610) Assess client for symptoms of general weakness, arm paralysis, and fatigue for planning methods. (Rationale: General weakness, arm paralysis
and fatigue were reported to be main causes of being unable to dress oneself. Independent W) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 702) Provide privacy and limit the number of people in the room. (Rationale: Privacy conveys respect and increases dressing ability. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 703) Select clothing in larger sizes, wide sleeves tshirts, or shirts that open in the front. (Rationale: Simplifying dressing tasks increases self care and safety, while decreasing exertion. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 703) Teach client to dress affected side first, then the unaffected side. (Rationale: Dressing the affected side first allows for easier manipulation of clothing Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 704) Teach the simplest in a task until mastered, and then proceed to more complicated steps. (Rationale: Simplifying dressing and grooming tasks that consist of many small steps promotes mastery. Independent S/.E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 705 ) Use careful aseptic technique when caring for wounds. (Rationale: client safety when performing aseptic technique is of the highest importance. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 497) Provide client with a complete balanced therapeutic diet after the immediately postoperative period. (Rationale: Improvement in nutritional status can improve outcome of postoperative period. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 497) Observe and report signs of infection such as redness, warmth, discharge and increase in body temp. (Rationale: Prospective surveillance study for nosocomial infection on hematologyoncology units should include fever of unknown origin as the single most common and clinically important entity. Independent WC) (Ackley and
Ladwig pg. 498) Assess for skin color, moisture, texture and turgor. (Rationale: The skin is the body’s first line of defense in protecting the body from infection. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 498) Encourage fluid intake. (Rationale: Fluid intake helps thin secretions and replaces fluid lost during surgery. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 498) Teach the client risk factors contributing to surgical wound infection, smoking. (Rationale: These are some of the factors associated with risk of surgical wound infection. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 499) Teach the client and family the symptoms of infection that should be promptly reported to a primary medical caregiver. (Rationale: two thirds of wound infections occur after discharge. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig, pg 450)
Discharge Planning-.5 Area of Concern A Activity:
M Medication:
Discharge Preparation Needed Instruct Pt to: Do not sign any legal papers or make any legal decisions for 24hrs after surgery. Rest the day of surgery. Place a pillow under your elbow: no pillow under your shoulder. Sleep in a semi-upright position in a recliner or propped up by pillows may also be helpful. Exercises: Perform early postop exercises as instructed by Dr. Burra. (Remove the strap of sling and perform range of motion exercises, gently of the elbow and straightening of the elbow, every hour that pt is awake. After performing exercises, place arm back in the sling and put the sling straps back on. Pt. may shower after 48hourse. Do not run water directly on the wound. After the shower remove the band aids, gently dad portal sires dry and apply fresh band aids. Do not submerge the shoulder in a pool (bathtub, hot tub etc.)Until the suture site has completely healed and stitches have been removed. Driving should be avoided and pt is not allowed to drive while wearing the sling, under the influence of pain medication, or when there is lack of sufficient strength to meet the requirements of driving a motor vehicle. Pt is advised against driving until further evaluation by Dr. Burra. No NSAIDS for risk of bleeding. (No Advil/No Aleve) Norco:1-2 325mg/10mg tabs PO PRN
E Environment:
Pt. will be going home.any hazards at home need to be addressed, any loss of limb use predisposes to fall risk.—sleeping arrangements, task reassignment, etc
T Treatment
Sling/Brace: The day of the surgery the arm will be placed in a sling/brace for comfort and protection. The sling/brace includes a waistband should be worn at all times, especially in bed. It may be intermittently removed, to shower, dress, and perform exercises. A cryotherapy (cooling) device or conventional ice pack will provide cold therapy to the shoulder and reduce pain and swelling. Use the cryotherapy 20min every hour on the first and second postoperative days. After that, the device may be used about 4-8 sessions per day, 20 min each. Additional instructions on the use of the device will be provided by Dr. Burra and the physical therapist. Do not place the cooling pad of the cyrotherapy device or the ice packs directly on the skin. Please use a barrier between the skin and the cooling device/ice packs.
H Health Teaching
O Outpatient Referral
D Diet
Dressings: remove outer dressings 36-48 hours after surgery. Leave in place any small adhesive Steri-strips or sutures that are directly on the incision. Apply Band Aids to the portal sites. Replace the Band aids every 24hrs and after a shower. Do not use bacitracin or any other ointments, extra dressing materials, sterile gauze and tape can be found at most pharmacy/drug stores. Normal Symptoms and findings after surgery: Shoulder pain and warmth is normal, bloody drainage and limited areas of numbness may be present around the incision, bruising and swelling distal to the shoulder may occur, low temperature (less 101.5 degrees F) is common after surgery, deep breathing exercises may be helpful. Notify Dr. Burra if: you develop fever greater than 101.5 degrees F, chills or night sweats, the wound turns red and drainage increases, the pain is not tolerable despite the use medication, if you develop numbness of tingling. An appointment should have been scheduled with physical therapy for the first day after surgery. Be certain that pt. brings a copy of specific physical therapy prescription to your first appointment. If the therapist is unsure of the protocol to be followed please have him Dr. Burra for appropriate instructions. Please return to Dr office in 10-14 days to have sutures removed. To call and make an Do not drink anything alcoholic for at least 24hrs after surgery. Gradually increase diet from soft foods to a regular diet as tolerated. In case of nausea avoid solid foods take only clear liquids as tolerated if persistent nausea or vomiting please your physician. FYI-an increase in calories aids in healing; malnourishment is a major cause for delayed surgical healing.
POWER COMPONENTS: _A__ Attention Span (Acute Limited attention span due to anesthesia) _A_ Energy Level (Acute decrease in energy level due to anesthesia) _A__ Control of body movements (Acute control loss due to anesthesia) _A__ Ability to reason (Acute ineffective ability to reason due to anesthesia) _A__ Ability to make decisions (Acute inability to make decisions due to anesthesia) _A__ Motivation (Acute deficit in motivation due to anesthesia) _A__ Knowledge of health problem (Patients knowledge deficit in removal of foreign body and where it came from is diminished) _A__ Ability to provide for self care (Acute inability to provide for self-care due to anesthesia and surgical incision) _A__ Skills needed to adapt self-care needs (Patient will difficulty with adapting to self care needs without the assistance of left arm while recovering) _A__ Ability to adapt self-care needs to A.D.L. (Patient will have difficulty with A.D.L.’s due to limited extremity movement.)
UNIVERSAL / HEALTH DEVIATION SELF-CARE REQUISITE ASSESSMENT: Air (Respiratory, Cardiovascular)-3 Preop: Bp: 109/73, Temp: 98.2, Apical Pulse: 64, regular and strong, Normal EKG, Respirations: 18, Easy on room air. Lung sounds: Bilaterally equal, No secretions, SaO2:98%, Capillary refill: <2 sec. Heart sounds: normal. Pt does not complain of chest pain but does state that he does have hypertension. Mucous membrane: moist, Nail bed color: Pink. Serum Lab results: Glucose: 85 Creatinine: 1.0 Serum Calcium: 9.7 Total bilirubin: 0.2 Alanine Aminotransfer: 32 AST: 16 Alkaline Phosphatase: 63 Chloride: 101 Carbon Dioxide: 28 Granulocyte percentage: 5.3 Granulocyte Absolute: 5.3 Lymph Percent: 26.5 Lymphocyte Absolute: 2.2 Monocyte Percent: 8.3 Monocyte Absolute: 0.7 Eosinophil Percent: 1.4 Eosinophil Absolute: 0.1 Basophil Percent: 0.2 Basophil Absolute: .0 WBC: 8.4 RBC: 4.71 Hemoglobin: 14.5 Hematocrit: 42.4 MCV: 90 MCH: 30.8 MCHC: 34.2 Platelets: 220 RDW: 13.2 PT: 10.3 PTT: 27.9 Pt. had chest x-ray done: Frontal and lateral projections of the chest demonstrate biapical pleural parenchymal scarring. Lung volumes show large but otherwise clear. Heart size within normal limits. Postop: Bp: 115/62 Apical pulse: 66 SaO2: 94% on room air, Lung sounds bilaterally equal. Resp:16 Radial pulse strong.. Warm temperature normal color of extremities. Sensation: numbness in left arm due to interscalene block. Extremities normal color, cap <2, no edema present. Water (Renal, F & E) Urine Clear yellow. Urinanalysis: Ph: 7.0 Specific Gravity: 1.003 Glucose: Negative Blood: Negative Ketones: Negative Protein: Negative Urobilinogen: <2.0mg Bilirubin: Negative Leukocyte Esterase: Negative Nitrate: Negative GFR: >=60 Sodium: 139 Potassium: 4.6 Total Protein: 7.9 Albumin: 4.6. Preop:1000ml IV Lactated Ringers, NPO Food / Elimination (Gastrointestinal) Abdomen soft, no masses,. Bowel sounds present in all four quadrants. Patient has crowns. No guarding or rebound. Skin turgor normal. Oropharynx pink and moist. Postop: pt ate 4 oreo cookies and had 3sips of pepsi. Activity & Rest (Musculoskeletal, Neurological) Pt. has limited ROM due to surgery, sleep patterns normal. Sensory and motor intact, PERRLA, pt. has pain and limited movement in L. arm due to Surgery. Pt. also complains of previous back pain for several months. Pt. denies sleep, anxiety, depression problems. Solitude & Social Interaction (Sensory Perception, Psychosocial) Pt. does not wear glasses. Interaction with family and friends is close and normal. No issues in communication. Pt. does not use antidepressants or anti-seizure medication. Prevention of Hazards (Endocrine Autoimmune, Chemical) Pt. smokes 1pack in two weeks. Alcohol consumption: 6pk in month, Seizures as child no longer has episodes. Home environment safe. Anesthesia istered during surgery: Versed, Fentanyl, Lidocain. Foreign body removed during surgery. Side rails up during transport. Dressings clean. Incision made at left anterior shoulder. No drainage noticed post operation. Promotion of Normalcy (Personal Hygiene, Self Concept, Reproductive, Integument) Preop: Skin intact no lesions. IV right anterior forearm Postop: patient had a Cuff IC and was unable to move arm. Pt had incision on left shoulder no drainage present. Patient confirmed of no anxiety feeling day of surgery. No anxiety was seen in facial expressions. Pain after surgery was at 0 (1-10 scale). Patient is able to complete ADL with assistance due to surgery.
DEVELOPMENTAL SELF CARE REQUISITES: Client’s Age: 32 Stage of Development: Generativity Vs. Self Absorption How might this illness interfere with the client’s developmental tasks: How might the client’s stage of development impact his/her adjustment to the illness? Erikson observed that middleage is when we tend to be occupied with creative and meaningful work issues surrounding out family. The significant task is to contribute to the betterment of society, which for the patient is now not able to do. The patient has to focus on himself to further increase his health and to provide an adequate amount of time for his surgery incisions to heal. This stage of development may impact the patient very easily. The patient is an eager and willing man and would to anything for his family, even if it did include not letting his shoulder rest after the surgery; prolonging the healing time.
Research of the Medical Diagnosis Arthroscopic Bicep Tenodesis: Arthroscopy is a procedure that allows direct visualization of a to diagnose t disorders. Treatment of tears, defects, and disease processes may be performed through the arthroscope. The procedure is performed through the arthroscope in an operating room, under sterile conditions. Injection of a local anesthetic agent into the t or general anesthesia is used. A large bore needle is inserted and the t is tended with saline. The arthroscope is introduced and t structures, synocium, and articular surfaces are visualized. After the procedure the puncture wound is closed with adhesive strips or sutures and covered with a sterile dressing. Complications are rare but may include infection, hemarthrosis, neurocascular compromise, thrombophlebitis, stiffness, effusion, adhesion, and delayed wound healing. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Bicept tendoesis: A biceps tenodesis is a procedure that cuts the normal attachment of the biceps tendon on the shoulder socket and reattaches the tendon to the bone of the humerus. By performing a biceps tenodesis, the pressure of the biceps attachment is taken off the cartilage rim of the shoulder socket (the labrum), and a portion of the biceps tendon can be surgically removed. Essentially a biceps tenodesis moves the attachment of the biceps tendon to a position that is out of the way of the shoulder t. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Nursing interventions: After the procedure, the t is wrapped with a compression dressing to control welling. In addition ice may be applied to control edema and enhance comfort. Frequently, the t is kept extended and elevated to reduce swelling. It is important to monitor and document the neurovascular status. Analgesic agents are istered as needed. The patient is instructed about activities and exercises that may be preformed. The patient and family are informed of symptoms to watch for in order to determine whether complications are occurring and of the importance of notifying the physician of this observation. (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010) Subacromial Bursectomy: is removal of the subscromial bursa sac (a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion at a pressure point in the body. near ts where tendons or muscles cross either bone or other muscles). (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, & Cheever, 2010)
Significance of Normal/Abnormal Diagnostic Tests Lab work: all levels are normal Urinanalysis: all levels are normal Chest X-ray: Frontal and lateral projections of the chest demonstrate biapical pleural parenchymal scarring. Lung volumes show large but otherwise clear. Heart size within normal limits. Medical Technologies: Treatments / Medications Clonazepan: 0.5mg, PRN Action: Depresses nerve impulse transmission in motor cortex. Rationale: Patient has anxiety with palpitations. Side effects: drowsiness, behavioral disturbances Nursing implications: assess for calm facial expression and decreased restlessness, assess vital signs. Atenolol: 25mg daily Action: Blocks beta-adrenergic receptors in cardiac tissue Rationale: Treatment of hypertension. Side Effects: Hypotension, dizziness, constipation Nursing Implications: Monitor B/P and pulse for bradycardia, and respirations for difficulty in breathing. Albuterol: 2 puffs q4 hrs PRN Action: Broncho dilator. Rationale: Patient has asthma but has not needed medication, and cannot the last time he has taken medication. Nursing Implications: Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations. Assess lungs for abnormal lung sounds.
Fluticasone Propionate: 2 puffs BID Action: Prevents and controls inflammation. Rationale: Patient has asthma but has not needed medication, and cannot last time he has taken medication. Nursing Implications: Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations. Assess lungs for abnormal lung sounds. Post OP ORDERS: Morphine: 2-4 mg every 2min IV PRN max dose: 20mg Action: binds with opioid receptors within CNS Rationale: Pain relief Nursing Implications: monitor vital signs 5-10 min after IV check for adequate voiding. Assess for clinical improvement. Fentanyl: 25-50 mcg every 2min IV PRN max dose: 100mcg Action: reducing stimuli from sensory nerve endings, inhibits ascending pain pathways Rationale: Pain relief Nursing Implications: Asst with ambulation, encourage post op turn, cough deep breathe q2h. Monitor Vital signs, assess for relief of pain Prochlorperazine: 10mg IM Action: Acts to block dopamine receptors in chemoreceptor trigger zone. Rationale: Relieves nausea/vomiting Nursing Implications: Monitor BP for hypotension. Monitor WBC count. Assess for therapeutic response. Onsansteron: 4mg IV Action: blocks serotonin, both peripherally on vagal nerve terminals, centrally in chemoreceptor trigger zone. Rationale: Relieves nausea/vomiting Nursing Implications: Assess for dehydration, assess bowel sounds for peristalsis, and assess mental status Meperidine: 12.5 IVP May repeat x1 Action: Binds to opoid receptors with in CNS Rationale: for shivering Nursing Implications: Monitor vitals 15-30 mins after subQ/IM dose, 5-10 mins after IV dose. Monitor pain level, bowel activity. Prioritized List of Nursing Diagnoses (in PES format Acute pain r/t injury in surgical care AEB pt. verbalization. Self-Care Deficit related to impaired ability to perform self-care tasks, as evidenced by statements of need for assistance and observed difficulty in performing activities of daily living Risk for infection r/t invasive procedure. Acute pain r/t presence of intubation tube AEB pt. verbalizing a mild sore throat. Acute back pain related to back injury as evidenced by patient verbalization. Ineffective health maintenance r/t lack of knowledge regarding prevention of dental disease AEB pt crowns. Risk for constipation r/t use anesthesia, decrease in fluid and food intake, and pain medication. Risk for ineffective breathing pattern r/t effects of narcotics and anesthesia. Risk for Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunction related to tissue trauma and Readiness for enhanced Therapeutic regimen management: expresses desire to learn measures to stop smoking.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS (NANDA)
Acute pain r/t injury in surgical care AEB pt. verbalization.
SELF-CARE AGENCY-1 Goal (NOC) + Expected Outcomes (NOC Indicators) NOC: Pt. will have a reduction in pain by discharge. NOC Indicators: Pt. will verbalize pain at a level of 3 or less by the 10/28.
NOt. knows an easier method for dressing . NOC Indicators: Pt. will verbalize three types of clothing that are easier to put on by 10/28.
Self-Care Deficit related to impaired ability to perform self-care tasks, as evidenced by statements of need for assistance and observed difficulty in performing activities of daily living Ok so you would Use selfcare deficit: dressing
Risk for infection r/t invasive procedure.
NOCindicator: Pt. will demonstrate the ability to dress. NOC Indicator: Pt. will know to dress the affected side first by 10/28.
Goal: Prevention of infection These are all indicators NOC: Pt. will know signs and symptoms of infection. NOC Indicator: Pt. will verbalize $ signs and symptoms of infection. NOC: Pt. will have surgical area that shows evidence of healing.at f/u visit
NURSE AGENCY (NIC) Nursing actions (NIC Activities) (Include rationales, Independent or Interdependent and S/E, PC, or WC) Assure patient attentive analgesic care: Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain, to include location, characteristics, onset/ duration, frequency, quality, intensity or severity of pain and precipitating factors. (Rationale: initial assessment and documentation provide direction for the pain treatment plan. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 604) Ask the client to describe past experiences with pain and the effectiveness of methods used to manage pain, including experiences with side effects, typical coping responses, and the way the client expresses pain. (Rationale: many patients harbor fears and misconceptions regarding the use of analgesics, management of side effects, and risk of addiction. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 606) Assess and document the intensity of the pain and discomfort after surgery. (Rationale: The clients report of pain is the single most reliable indicator of pain. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig [g 605) Obtain a prescription to ister and opioid. Rationale: opioid analgesics are indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain Interdependent PWC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 607) ister opioids orally or IV as ordered when appropriate and available. (Rationale: the least invasive route of istration capable of providing adequate pain control is recommended. Independent PC )(Ackley and Ladwig pg 608) When opioids are istered, assess pain intensity, sedation, and respiratory status at regular intervals. (Rationale: Opioids may cause
EVALUATION AND/OR MODIFICATIONS
Patient had reached goal, by the time of discharge patient confirmed a level of 2 out of 10 on the pain scale. Patient also verbalized the importance of not waiting till the pain was intolerable before taking the medication. Patient had reached goal: patient verbalized three easier steps of dressing that are easier to put on. (Wide sleeve shirts, sweaters that zip up in front, and dressing the affected arm first.) Patient had reached goal and indicated 5 signs and symptoms of infection. (Pain, Redness, Heat, Fever)purulentdrainage? Patient had reached goal, by the time of discharge patient did not show any signs of redness or swelling in the surgical area. Patient had reached goal. Patient verbalized the steps in correct hand hygiene, indicated the when time of surgical dressing had to be changed, and indicated to whomever was doing the dressing change required to wear gloves.
NOC Indicators: Pt. will have no redness and drainage by 10/30 and none at f/u visit NOC: Pt. will know how to change dressing. NOC Indicators: Patients will wash hands, wear gloves and apply
clean band aids to sutures.
respiratory depression because they reduce the responsiveness of carbon dioxide chemoreceptors located in the respiratory centers of the brain. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 609) Teach and implement non-pharmacological interventions when pain is relatively well controlled with pharmacological interventions. (Rationale: non-pharmacological interventions should be used to supplement, not replace, pharmacological interventions Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 609) Reinforce the importance of taking pain medications to keep pain under control. (Rationale: teaching clients to stay on top of their pain and prevent it from getting out of control improves the ability to accomplish the goals of recovery. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 610) Assess client for symptoms of general weakness, arm paralysis, and fatigue for planning methods. (Rationale: General weakness, arm paralysis
and fatigue were reported to be main causes of being unable to dress oneself. Independent W) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 702) Provide privacy and limit the number of people in the room. (Rationale: Privacy conveys respect and increases dressing ability. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 703) Select clothing in larger sizes, wide sleeves tshirts, or shirts that open in the front. (Rationale: Simplifying dressing tasks increases self care and safety, while decreasing exertion. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 703) Teach client to dress affected side first, then the unaffected side. (Rationale: Dressing the affected side first allows for easier manipulation of clothing Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 704) Teach the simplest in a task until mastered, and then proceed to more complicated steps. (Rationale: Simplifying dressing and grooming tasks that consist of many small steps promotes mastery. Independent S/.E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg. 705 ) Use careful aseptic technique when caring for wounds. (Rationale: client safety when performing aseptic technique is of the highest importance. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 497) Provide client with a complete balanced therapeutic diet after the immediately postoperative period. (Rationale: Improvement in nutritional status can improve outcome of postoperative period. Independent PC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 497) Observe and report signs of infection such as redness, warmth, discharge and increase in body temp. (Rationale: Prospective surveillance study for nosocomial infection on hematologyoncology units should include fever of unknown origin as the single most common and clinically important entity. Independent WC) (Ackley and
Ladwig pg. 498) Assess for skin color, moisture, texture and turgor. (Rationale: The skin is the body’s first line of defense in protecting the body from infection. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 498) Encourage fluid intake. (Rationale: Fluid intake helps thin secretions and replaces fluid lost during surgery. Independent WC) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 498) Teach the client risk factors contributing to surgical wound infection, smoking. (Rationale: These are some of the factors associated with risk of surgical wound infection. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig pg 499) Teach the client and family the symptoms of infection that should be promptly reported to a primary medical caregiver. (Rationale: two thirds of wound infections occur after discharge. Independent S/E) (Ackley and Ladwig, pg 450)
Discharge Planning-.5 Area of Concern A Activity:
M Medication:
Discharge Preparation Needed Instruct Pt to: Do not sign any legal papers or make any legal decisions for 24hrs after surgery. Rest the day of surgery. Place a pillow under your elbow: no pillow under your shoulder. Sleep in a semi-upright position in a recliner or propped up by pillows may also be helpful. Exercises: Perform early postop exercises as instructed by Dr. Burra. (Remove the strap of sling and perform range of motion exercises, gently of the elbow and straightening of the elbow, every hour that pt is awake. After performing exercises, place arm back in the sling and put the sling straps back on. Pt. may shower after 48hourse. Do not run water directly on the wound. After the shower remove the band aids, gently dad portal sires dry and apply fresh band aids. Do not submerge the shoulder in a pool (bathtub, hot tub etc.)Until the suture site has completely healed and stitches have been removed. Driving should be avoided and pt is not allowed to drive while wearing the sling, under the influence of pain medication, or when there is lack of sufficient strength to meet the requirements of driving a motor vehicle. Pt is advised against driving until further evaluation by Dr. Burra. No NSAIDS for risk of bleeding. (No Advil/No Aleve) Norco:1-2 325mg/10mg tabs PO PRN
E Environment:
Pt. will be going home.any hazards at home need to be addressed, any loss of limb use predisposes to fall risk.—sleeping arrangements, task reassignment, etc
T Treatment
Sling/Brace: The day of the surgery the arm will be placed in a sling/brace for comfort and protection. The sling/brace includes a waistband should be worn at all times, especially in bed. It may be intermittently removed, to shower, dress, and perform exercises. A cryotherapy (cooling) device or conventional ice pack will provide cold therapy to the shoulder and reduce pain and swelling. Use the cryotherapy 20min every hour on the first and second postoperative days. After that, the device may be used about 4-8 sessions per day, 20 min each. Additional instructions on the use of the device will be provided by Dr. Burra and the physical therapist. Do not place the cooling pad of the cyrotherapy device or the ice packs directly on the skin. Please use a barrier between the skin and the cooling device/ice packs.
H Health Teaching
O Outpatient Referral
D Diet
Dressings: remove outer dressings 36-48 hours after surgery. Leave in place any small adhesive Steri-strips or sutures that are directly on the incision. Apply Band Aids to the portal sites. Replace the Band aids every 24hrs and after a shower. Do not use bacitracin or any other ointments, extra dressing materials, sterile gauze and tape can be found at most pharmacy/drug stores. Normal Symptoms and findings after surgery: Shoulder pain and warmth is normal, bloody drainage and limited areas of numbness may be present around the incision, bruising and swelling distal to the shoulder may occur, low temperature (less 101.5 degrees F) is common after surgery, deep breathing exercises may be helpful. Notify Dr. Burra if: you develop fever greater than 101.5 degrees F, chills or night sweats, the wound turns red and drainage increases, the pain is not tolerable despite the use medication, if you develop numbness of tingling. An appointment should have been scheduled with physical therapy for the first day after surgery. Be certain that pt. brings a copy of specific physical therapy prescription to your first appointment. If the therapist is unsure of the protocol to be followed please have him Dr. Burra for appropriate instructions. Please return to Dr office in 10-14 days to have sutures removed. To call and make an Do not drink anything alcoholic for at least 24hrs after surgery. Gradually increase diet from soft foods to a regular diet as tolerated. In case of nausea avoid solid foods take only clear liquids as tolerated if persistent nausea or vomiting please your physician. FYI-an increase in calories aids in healing; malnourishment is a major cause for delayed surgical healing.