Nursing Responsibilities In Blood Transfusion 1u1o2a
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3i3n4
Overview 26281t
& View Nursing Responsibilities In Blood Transfusion as PDF for free.
More details 6y5l6z
- Words: 1,064
- Pages: 5
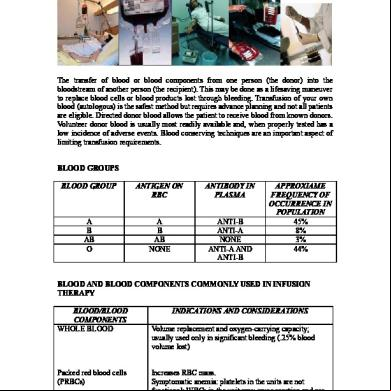
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES IN BLOOD TRANSFUSION Patient’s Expectation of Nurses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Courtesy Care Patience Clarity of instructions Promptness in answering call bells Provision of information Patient confidentiality Competence
Purpose of Blood istration 1. 2. 3. 4.
Increase blood volume Replace certain blood constituent Replace hemoglobin Supply an antibody
Definition of Responsibilities in BT • Hospital Management – Ensure that there is senior management commitment to better BT – Ensure appropriate hip & function of the Hospital Transfusion Committee – Ensure appropriate BT policies are in place, implemented & monitored • Hospital Transfusion Committee – Promote best practice thru local protocols based on national guidelines – Lead the audit of the practice of BT against the hospital policy & national guidelines – ing of audit & modify existing protocols as needed • Medical Staff – Are solely responsible for prescribing blood, blood components & blood products & for ensuring adequate documentation of BT in the medical notes – Responsible for informing the patient of: • Indication for the BT • Risks & benefits • Right to refuse BT • Alternatives to BT • Medical/Nursing Staff – Request blood, blood components & blood products – Carry out the procedure for the istration of blood & blood components – Monitor patients during the transfusion & carry out appropriate actions in the event of adverse reactions
– Report reactions or other incidents R/T transfusion • Phlebotomists – Take blood samples for blood grouping & compatibility testing provided they have been given for formal training & have completed competency assessment Considerations prior to transfusion • Positive identification of patient is essential & must be based on the following: – Questioning the patient by asking surname, first name & date of birth – Checking that the details on the patient’s identification match those on the request form – For an unidentified patient the patient identification no. and gender are minimum patient identifiers • Venipuncture: - Only one patient must be punctured at a time to minimize the risk of error • Sample labelling – Sample tube details must be handwritten by the person extracting the sample, done at bedside – Sample must not be pre-labelled • Telephone requests - hospital blood bank must have a policy for documenting telephone requests - identity of the person making the request & the person receiving must be recorded - the following information must be provided: - patient’s surname, first name & patient’s case no. - number & type of blood or blood components required including any special requirements - reason for the request - time & date the blood or blood components are required • Blood must not be stored in ward or domestic refrigerators • Blood must only be stored or transported in boxes designated for this purpose • Staff removing blood from bank/lab must have documentation containing the patient’s identification details • When blood or blood components are delivered to a ward or OR a member of appropriately trained staff must check that the correct blood has been delivered by checking the patient identification details • Normally one unit of blood or blood components is to be collected at a time unless rapid infusion is anticipated • Blood & blood components are considered as medicines for istration purposes, thus, must only be istered by a ed physician or nurse • Two RNs must check the identity of the patient & the unit of blood. • Identity check of patient & unit of blood must take place at patient’s bedside • prior to transfusion, PNSS may be prescribed by the physician
Technical aspects in the istration of blood & blood components • When blood is received in the clinical area, transfusion must start as soon as possible (within 30 min) • Blood for transfusion must be stored in a designated blood ref at stable temp 2-6 C. If a unit of blood has been out of the ref for more than 30 min & there is no imminent transfusion, the unit must be returned to blood bank immediately • Blood must be transfused through a sterile set • Electronic infusion pumps may damage blood cells, & must not be used for the istration of red cells • The size of cannula should depend on the size of the vein & the speed at which blood is to be transfused • Blood is not routinely warmed. • Drugs must not be added to blood under any circumstances • A single unit must be transfused in a maximum time of 4 hours • istration set must be continuously used in a maximum of 12 hrs to prevent bacterial growth • Empty blood bags must be returned to the laboratory ASAP after the transfusion Care & Monitoring of Transfused Patients • Nursing staff are responsible for the care & monitoring of patients receiving a transfusion • Visual observation of the patient throughout transfusion is an essential assessment • V/S related to the transfusion must be recorded separately from routine observations & clearly dated, or recorded – Temp, pulse, BP, RR at the start & end – Temp, pulse, BP, RR 15 min after starting Documentation Recommendation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Site Baseline V/S Time started & terminated Type of blood product & ID no. Signatures of person initiating & ing product. Total no. of units, volume of blood & saline infused. Pre/Post medication used for blood therapy Patient’s response / reactions All nursing interventions iniated & performed during therapy.
Troubleshooting Tips
Sluggish IV lines & clogged filters that decrease the flow rate may be encountered during transfusion. Investigations include: • Is there a kink in the set? • Is the correct gauge of needle / catheter being used? • Has irrigation with normal saline been attempted? • Has the filter been used for more than 2 units? • Has the blood bag been rotated to distribute contents evenly? • Is the bag 36-48” above site? • Does the roller clamp need to be adjusted? If all negative, consider use of pressure cuff. Reactions to Transfusion Reactions
Cause
Assessment
Interventions
Allergic reaction
Antibody reactions to allergens in donor’s blood
Mild: hives, itching, Mild: Slow BT, Notify flushing Dr., ister Severe: Shortness of antihistamine as breath, ordered. bronchospasm, Severe: Stop BT, wheezing Maintain IV line, Notify Dr., Give antihistamine, epenephrine Prevention: Antihistamine 1 hr before BT
Courtesy Care Patience Clarity of instructions Promptness in answering call bells Provision of information Patient confidentiality Competence
Purpose of Blood istration 1. 2. 3. 4.
Increase blood volume Replace certain blood constituent Replace hemoglobin Supply an antibody
Definition of Responsibilities in BT • Hospital Management – Ensure that there is senior management commitment to better BT – Ensure appropriate hip & function of the Hospital Transfusion Committee – Ensure appropriate BT policies are in place, implemented & monitored • Hospital Transfusion Committee – Promote best practice thru local protocols based on national guidelines – Lead the audit of the practice of BT against the hospital policy & national guidelines – ing of audit & modify existing protocols as needed • Medical Staff – Are solely responsible for prescribing blood, blood components & blood products & for ensuring adequate documentation of BT in the medical notes – Responsible for informing the patient of: • Indication for the BT • Risks & benefits • Right to refuse BT • Alternatives to BT • Medical/Nursing Staff – Request blood, blood components & blood products – Carry out the procedure for the istration of blood & blood components – Monitor patients during the transfusion & carry out appropriate actions in the event of adverse reactions
– Report reactions or other incidents R/T transfusion • Phlebotomists – Take blood samples for blood grouping & compatibility testing provided they have been given for formal training & have completed competency assessment Considerations prior to transfusion • Positive identification of patient is essential & must be based on the following: – Questioning the patient by asking surname, first name & date of birth – Checking that the details on the patient’s identification match those on the request form – For an unidentified patient the patient identification no. and gender are minimum patient identifiers • Venipuncture: - Only one patient must be punctured at a time to minimize the risk of error • Sample labelling – Sample tube details must be handwritten by the person extracting the sample, done at bedside – Sample must not be pre-labelled • Telephone requests - hospital blood bank must have a policy for documenting telephone requests - identity of the person making the request & the person receiving must be recorded - the following information must be provided: - patient’s surname, first name & patient’s case no. - number & type of blood or blood components required including any special requirements - reason for the request - time & date the blood or blood components are required • Blood must not be stored in ward or domestic refrigerators • Blood must only be stored or transported in boxes designated for this purpose • Staff removing blood from bank/lab must have documentation containing the patient’s identification details • When blood or blood components are delivered to a ward or OR a member of appropriately trained staff must check that the correct blood has been delivered by checking the patient identification details • Normally one unit of blood or blood components is to be collected at a time unless rapid infusion is anticipated • Blood & blood components are considered as medicines for istration purposes, thus, must only be istered by a ed physician or nurse • Two RNs must check the identity of the patient & the unit of blood. • Identity check of patient & unit of blood must take place at patient’s bedside • prior to transfusion, PNSS may be prescribed by the physician
Technical aspects in the istration of blood & blood components • When blood is received in the clinical area, transfusion must start as soon as possible (within 30 min) • Blood for transfusion must be stored in a designated blood ref at stable temp 2-6 C. If a unit of blood has been out of the ref for more than 30 min & there is no imminent transfusion, the unit must be returned to blood bank immediately • Blood must be transfused through a sterile set • Electronic infusion pumps may damage blood cells, & must not be used for the istration of red cells • The size of cannula should depend on the size of the vein & the speed at which blood is to be transfused • Blood is not routinely warmed. • Drugs must not be added to blood under any circumstances • A single unit must be transfused in a maximum time of 4 hours • istration set must be continuously used in a maximum of 12 hrs to prevent bacterial growth • Empty blood bags must be returned to the laboratory ASAP after the transfusion Care & Monitoring of Transfused Patients • Nursing staff are responsible for the care & monitoring of patients receiving a transfusion • Visual observation of the patient throughout transfusion is an essential assessment • V/S related to the transfusion must be recorded separately from routine observations & clearly dated, or recorded – Temp, pulse, BP, RR at the start & end – Temp, pulse, BP, RR 15 min after starting Documentation Recommendation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Site Baseline V/S Time started & terminated Type of blood product & ID no. Signatures of person initiating & ing product. Total no. of units, volume of blood & saline infused. Pre/Post medication used for blood therapy Patient’s response / reactions All nursing interventions iniated & performed during therapy.
Troubleshooting Tips
Sluggish IV lines & clogged filters that decrease the flow rate may be encountered during transfusion. Investigations include: • Is there a kink in the set? • Is the correct gauge of needle / catheter being used? • Has irrigation with normal saline been attempted? • Has the filter been used for more than 2 units? • Has the blood bag been rotated to distribute contents evenly? • Is the bag 36-48” above site? • Does the roller clamp need to be adjusted? If all negative, consider use of pressure cuff. Reactions to Transfusion Reactions
Cause
Assessment
Interventions
Allergic reaction
Antibody reactions to allergens in donor’s blood
Mild: hives, itching, Mild: Slow BT, Notify flushing Dr., ister Severe: Shortness of antihistamine as breath, ordered. bronchospasm, Severe: Stop BT, wheezing Maintain IV line, Notify Dr., Give antihistamine, epenephrine Prevention: Antihistamine 1 hr before BT