Residual Risk Reduction (r3) w4s18
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3i3n4
Overview 26281t
& View Residual Risk Reduction (r3) as PDF for free.
More details 6y5l6z
- Words: 1,213
- Pages: 42
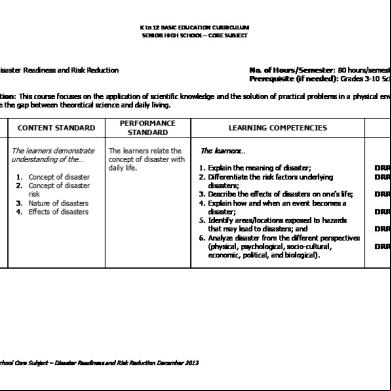
Risk Assessment Tool Residual Risk Reduction (R3) Danny Viator Superior Energy Broussard, LA
Tony Spencer Liberty Mutual Metairie, LA April, 2010
Definition-Residual Risk Reduction A process that involves a study to: – Analyze jobs – Identify hazards and existing controls – Determine the level of risk – Identify controls to reduce risk – Measure the amount of risk reduction
Some Facts About Risk • An inherent feature of systems; a quality that always exists to some degree • Is definable in of three factors (Frequency, Likelihood, & Severity) • Once it is defined, it can be quantified • The quantity of risk can be changed by changing these factors
The Risk “Factors” • Frequency (Exposure Opportunity) – How often the exposure exists
• Likelihood (Chance of Occurrence)
• Severity (Degree of Harm) – Worst Plausible scenario
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
< once per shift or day
2
> once per shift or day
3
> once per hour
4
> once per five minutes
5
At all times
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
Impossible
2
Unlikely
3
Possible
4
Probable
5
Multiple
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
First Aid
2
Medical Treatment
3
Lost time, full recovery
4
Some permanent impairment
5
Major permanent impairment or death
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
< once per shift or day
Impossible
First Aid
2
> once per shift or day
Unlikely
Medical Treatment
3
> once per hour
Possible
Lost time, full recovery
4
> once per five minutes
Probable
Some permanent impairment
5
At all times
Multiple
Major permanent impairment or death
Risk = F x L x S The quantity of risk can be changed by changing the risk “factors” – Eliminating a step – Changing how a step is done – Implementing new/revised controls
Organizing the R3 Team • Team leader -Familiar with the mechanics of R3 -Can facilitate group decision making • Group-Multi-disciplinary -Health & Safety -Operations -Engineering
R3 Example
Climbing & Working on Production Christmas Trees
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Production Tree R3 Team -Warren-Corporate Safety -Tony-Ins LC -Danny-Division Safety -Terry-Broker -John-Division Safety -Clint-Falls Rep -Joe-Division Safety -Joe P-Trainer -Spencer-Training Director
R3TM Baseline Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May, 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Orientation, JSEA, Work Boots, Clean Tree, 3 Pt Climbing, Dedicated Climbing Training, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
4
3
4
48
Risk Index1
48
F L S Risk
Risk Index2
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Subsequent Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May, 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls
F L S
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Risk Index1
Risk
New Controls
F L S Risk
All of the controls in the Baseline Assessment plus Job Specific Fall Protection Procedures
4
2
2
16
Risk Index2
16
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Worksheet Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
F L S Risk
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Orientation, JSEA, Work Boots, Clean Tree, 3 Pt Climbing, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
4
4
3
4
48
Risk Index1
48
All of the controls in the Baseline Assessment plus Job Specific Fall Protection Procedures
2
2
16
Risk Index2
16
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
Overview of Tree
Use of Fall Protection
Production Tree Residual Risk Reduction R3 = [(RI1 – RI2)/RI1 X100] = % Reduction 48-16 48x100
= 67% Reduction
R3 Example
Wire Sticks While Reaming Packing
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Wire Sticks R3 Team -Warren-Corporate Safety -Tony-Ins LC -Danny-Division Safety -John-Division Safety -Ryan-Division Safety -Matt-Corporate Safety -Robert-Operations -BJ-Training
R3TM Baseline Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
New employee orientation, JSA’s, Safety meetings, Kong Gloves, Pig tail & vice procedure recommended, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
5
4
3
60
Risk Index
60
Poster 3
F L S Risk
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Subsequent Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls
F L S Risk New Controls
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
All controls listed in the Baseline assessment plus packing mfg to ream out to 0.125 (vs.0.092), shop to ream out to 0.125, supply ream assist tool to all field operators, add JSA on reaming specifics, safety meeting emphasis on for next 90 days on these controls by field safety staff
Risk Index
F L S Risk 5
2
1
10
10
R3TM Worksheet Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
F L S Risk
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
New employee orientation, Kong Gloves, Pig tail & vice procedure recommended, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
5
5
4
3
60
Risk Index
60
All controls listed in the Baseline assessment plus packing mfg to ream out to 0.125 (vs.0.092), shop to ream out to 0.125, supply ream assist tool to all field operators, add JSA on reaming specifics, safety meeting emphasis on for next 90 days on these controls by field safety staff
2
1
10
10
Assist Tool
Assist Tool
Residual Risk Reduction R3 = [(RI1 – RI2)/RI1 X100] = % Reduction 60-10 60x100
= 83% Reduction
R3 Analysis Define the F-L-S scales
Identify New controls
Implement the new controls
Define the system to be studied (Activity)
“Score” each concern on the F-L-S scales
“Re-score” the concerns with the new controls
Identify the concerns to be analyzed (Incidents)
Identify/Analyze controls
Report the “R3” as a Safety Outcome!
Other R3 Examples • • •
Handling Chicksan pipe Vehicle traffic flow pattern in an oilfield yard Climbing on/off of vacuum tank trailers
• • •
Working on a burn table at a mfg plant Changing catalyst in a cat cracker Access to bucket truck by Linemen
So What’s In It For Me? • R3 provides a means for “examining systems” • R3 gets the people closest to the risk in systems involved in it’s reduction • It illustrates how interventions affect risk • It provides both upstream & downstream measures for safety efforts • R3 motivates action to reduce risk from hazards in systems
Tony Spencer Liberty Mutual Metairie, LA April, 2010
Definition-Residual Risk Reduction A process that involves a study to: – Analyze jobs – Identify hazards and existing controls – Determine the level of risk – Identify controls to reduce risk – Measure the amount of risk reduction
Some Facts About Risk • An inherent feature of systems; a quality that always exists to some degree • Is definable in of three factors (Frequency, Likelihood, & Severity) • Once it is defined, it can be quantified • The quantity of risk can be changed by changing these factors
The Risk “Factors” • Frequency (Exposure Opportunity) – How often the exposure exists
• Likelihood (Chance of Occurrence)
• Severity (Degree of Harm) – Worst Plausible scenario
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
< once per shift or day
2
> once per shift or day
3
> once per hour
4
> once per five minutes
5
At all times
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
Impossible
2
Unlikely
3
Possible
4
Probable
5
Multiple
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
First Aid
2
Medical Treatment
3
Lost time, full recovery
4
Some permanent impairment
5
Major permanent impairment or death
Risk Rating Scale Rating Frequency Likelihood Severity 1
< once per shift or day
Impossible
First Aid
2
> once per shift or day
Unlikely
Medical Treatment
3
> once per hour
Possible
Lost time, full recovery
4
> once per five minutes
Probable
Some permanent impairment
5
At all times
Multiple
Major permanent impairment or death
Risk = F x L x S The quantity of risk can be changed by changing the risk “factors” – Eliminating a step – Changing how a step is done – Implementing new/revised controls
Organizing the R3 Team • Team leader -Familiar with the mechanics of R3 -Can facilitate group decision making • Group-Multi-disciplinary -Health & Safety -Operations -Engineering
R3 Example
Climbing & Working on Production Christmas Trees
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Production Tree Examples
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Production Tree R3 Team -Warren-Corporate Safety -Tony-Ins LC -Danny-Division Safety -Terry-Broker -John-Division Safety -Clint-Falls Rep -Joe-Division Safety -Joe P-Trainer -Spencer-Training Director
R3TM Baseline Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May, 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Orientation, JSEA, Work Boots, Clean Tree, 3 Pt Climbing, Dedicated Climbing Training, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
4
3
4
48
Risk Index1
48
F L S Risk
Risk Index2
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Subsequent Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May, 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls
F L S
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Risk Index1
Risk
New Controls
F L S Risk
All of the controls in the Baseline Assessment plus Job Specific Fall Protection Procedures
4
2
2
16
Risk Index2
16
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Worksheet Facility: Superior Wireline Division
Exposure: Falls While Working on Production Trees
System: Production Trees
Date: May 2009
Task: Evaluating the task of climbing and working on production trees Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
F L S Risk
Employees exposed to falls while either climbing up or down production trees
Orientation, JSEA, Work Boots, Clean Tree, 3 Pt Climbing, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
4
4
3
4
48
Risk Index1
48
All of the controls in the Baseline Assessment plus Job Specific Fall Protection Procedures
2
2
16
Risk Index2
16
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
Overview of Tree
Use of Fall Protection
Production Tree Residual Risk Reduction R3 = [(RI1 – RI2)/RI1 X100] = % Reduction 48-16 48x100
= 67% Reduction
R3 Example
Wire Sticks While Reaming Packing
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Exposure Example
Wire Sticks R3 Team -Warren-Corporate Safety -Tony-Ins LC -Danny-Division Safety -John-Division Safety -Ryan-Division Safety -Matt-Corporate Safety -Robert-Operations -BJ-Training
R3TM Baseline Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
New employee orientation, JSA’s, Safety meetings, Kong Gloves, Pig tail & vice procedure recommended, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
5
4
3
60
Risk Index
60
Poster 3
F L S Risk
©Liberty Mutual NMLP
R3TM Subsequent Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls
F L S Risk New Controls
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
All controls listed in the Baseline assessment plus packing mfg to ream out to 0.125 (vs.0.092), shop to ream out to 0.125, supply ream assist tool to all field operators, add JSA on reaming specifics, safety meeting emphasis on for next 90 days on these controls by field safety staff
Risk Index
F L S Risk 5
2
1
10
10
R3TM Worksheet Division-Superior Wireline DivisionSlickline
Exposure-Wire Sticks
System-Stuffing Box Packing
Date-October, 2009
Task-Evaluating the task of reaming out stuffing box packings Concern
Current Controls F L S Risk New Controls
F L S Risk
Slickline Operators and Helpers are exposed to receiving wire sticks in the hands while they are reaming out stuffing box packings
New employee orientation, Kong Gloves, Pig tail & vice procedure recommended, Stop Work Authority, Behavior Based Safety
5
5
4
3
60
Risk Index
60
All controls listed in the Baseline assessment plus packing mfg to ream out to 0.125 (vs.0.092), shop to ream out to 0.125, supply ream assist tool to all field operators, add JSA on reaming specifics, safety meeting emphasis on for next 90 days on these controls by field safety staff
2
1
10
10
Assist Tool
Assist Tool
Residual Risk Reduction R3 = [(RI1 – RI2)/RI1 X100] = % Reduction 60-10 60x100
= 83% Reduction
R3 Analysis Define the F-L-S scales
Identify New controls
Implement the new controls
Define the system to be studied (Activity)
“Score” each concern on the F-L-S scales
“Re-score” the concerns with the new controls
Identify the concerns to be analyzed (Incidents)
Identify/Analyze controls
Report the “R3” as a Safety Outcome!
Other R3 Examples • • •
Handling Chicksan pipe Vehicle traffic flow pattern in an oilfield yard Climbing on/off of vacuum tank trailers
• • •
Working on a burn table at a mfg plant Changing catalyst in a cat cracker Access to bucket truck by Linemen
So What’s In It For Me? • R3 provides a means for “examining systems” • R3 gets the people closest to the risk in systems involved in it’s reduction • It illustrates how interventions affect risk • It provides both upstream & downstream measures for safety efforts • R3 motivates action to reduce risk from hazards in systems