Revised Sbm Assessment Tool.docx 5d391j
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3i3n4
Overview 26281t
& View Revised Sbm Assessment Tool.docx as PDF for free.
More details 6y5l6z
- Words: 1,662
- Pages: 5
REVISED SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT ASSESSMENT TOOL (Version 1. as of August 5, 2012)
Part I: Introduction The Revised School-Based Management (SBM) Assessment tool is guided by the four principles of ACCESs (A Childand Community- Centered Education System). The indicators of SBM practice were contextualized from the ideals of an ACCESs school system. The unit of analysis is the school system, which may be classified as beginning, developing or advanced (accredited level). The SBM practice is ascertained by the existence of structured mechanisms, processes and practices in all indicators. A team of practitioners and experts from the district, division, region and central office validates the self-study/assessment before a level of SBM practice is established. The highest level- “advanced” is a candidacy for accreditation after a team of external validators confirmed the evidence of practices and procedures that satisfies quality standards. Part II: Basic School/Learning Center (LC) Information: School/Learning Center: Region/Division: Name of School Head/LC Head: Address: Part III: Instruction to the s: Please indicate using a check mark the extent of SBM practice for each indicator listed below (numbered) based on the validation team’s consensual agreements after systematic D-O-D (Document Analysis-Observation-Discussion). For indicators with no evidence, indicate zero. Part IV: Rating Scale: 0 No evidence 1 Evidence indicates beginning structures and mechanisms are in place to demonstrate ACCESs 2 Evidence indicates planned practices and procedures are fully implemented and aligned to ACCESs 3 Evidence indicates practices and procedure satisfy quality standards Page 1 of 5
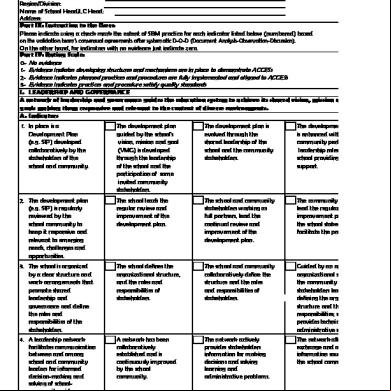
D. Management of Resources 1 2 3 8. Learners are equipped with Learners Learners Learners Resources are collectively A. Leadership and essential knowledge, skills, accomplish demonstrate demonstratehigh level and judiciously mobilized and Governance and values to assume minimum progressive of attainment of managed with transparency, A network of that system 3. leadership The ability Community Community A communityresponsibility and proficiency levels in improvements desired competencies effectiveness, and efficiency. provides the vision and that is owned for by their the own stakeholders are stakeholders accepted ability all aspects ofare the beyondinventory the minimum and life skills. Regular resource Stakeholders Resource Resource inventories direction to 1. the education community is invited to participate contribute to the of ability system learning. desired level of attainment is aware that a regular ischaracterized by are systemically system makinginventory it relevant continuously enhanced in setting up an development of an effects continuous competencies. competencies. collaboratively resource inventory is regularity, increased developed and and responsive to the to ensure that ability ability system improvement in the undertaken by learning available and is used participation by stakeholders are contexts C. of diverse management structures system for schoolcoversboth schoolmanagement of ability and managers, learning as the basis for stakeholders, and engaged in a communities. and mechanisms are based management based learning. Continuous Improvement facilitators, and community resource allocation communicated to the collaborative process 1. There isAinclear, place a mechanism In place is a The VMG is used The mechanism responsive transparent, to the emerging processes, andcommunity-wide stakeholders as basis for mechanism and mobilization. community that allows for the that collaboratively by as the empowers to themake decisions on inclusive, learning andresponsive needs and structures and managementof resource allocation andallows for the allocation development of a shared the schoolbasis and for resourcecommunityresource to lead not ability demands of system the community. is in mechanisms. education. mobilization. allocation vision,place, mission, and development of VMG community as guide and only in the and mobilization. collaboratively mobilization. goals(VMG) which by reflects by the school programs. aredevelopment of the 4. ability assessment Theand school, with in initiating Stakeholders Stakeholders developed community 2. There is a regular Stakeholders are Stakeholders Stakeholders the aspirations and thrusts of monitors communitytheparticipation . criteria and tools, of engaged in the VMG but incontinuously and stakeholders, which dialogue for planning invited to participate regularly engaged in collaborate to ensure the community. mechanisms, and stakeholders, development andmakingprograms collaboratively review expected and actual and resource in the development the planning andguided by community timely and need-based information collection and articulates an operation of an and enhance performance, continually programming, that is of educational plan resource and resource aspirationsplanning and thrusts. validation ability appropriate ability addresses the techniques gaps, and and accessible and inclusive, with resource programming and programming and processes arefor inclusive assessment ability systems’ processes, ensures a venue to continuously engageThe school, programming andThe schoolactively participate inschool 2. The organization’s vision, vision, vision, The vision, continuous and collaboratively framework with basic assessment system. mechanisms and and redress. stakeholders and direction, participate in the the and implementation of implementation of the direction, and aspirations are and direction, direction and 1. developed Roles and responsibilities and agreed of There components, is an active The stakeholders are Shared tools.and participatory implementation of aspirationsimplementation. the education plan. education plan. periodically the revisited and are in aspirations are aspirations are able upon. (PROCESS) person/s and party including that initiates engaged in clarifying processes of education place but there’s no adjusted by community the learning reviewed and reviewed regularly to collective body/ies are clarification implementation of the and defining their determiningroles, plans. facilitators, managers, learning plan yet on how to adjusted sometimes adjust and make them clearly definedand roles guidelines. specific roles and responsibilities, and and community stakeholders keep them responsive to respond to responsive to 5. Participatory School initiated Collaborative conduct School-communityagreed upon by andresponsibilities in responsibilities. abilities of is in place a Stakeholders Stakeholders areconditions and Stakeholders sustain to respond3.toThere the community’s to changes in the conditions and assessment of periodic performance of performance developed community stakeholders. educationdelivery. stakeholders in community-developed judicious, share the implementation conditions and emerging emerging engaged needs. andinforms emerging performance needs. performance is done environment. assessments which assessment managing resource management appropriate, and expertise in the and improvement of a needs. regularly with the involve participation planning, plan assessment is anding system that drives effective use of Dialogues and collaborative collaboratively 3. Stakeholders actively Dialogues and Dialogues and community. Assessment of stakeholders. adjustments and practiced and is the education. appropriate behaviors consensus of resources. development of consensus developed, participate, through are seldom consensus are often are always 2. A results chievement and lessons of goals learned is Performance A community-level requirements for basis A communityfor improving the stakeholders to ensure resource periodically adjusted, dialogue and/or consensusused in formulating used in formulating used in formulating recognized serve as basis based for , on a ability is ability technical assistance. system monitoring accepted performance and judicious, appropriate, school and policies and management system. and and constituent building, in formulating school policies and school policies collaboratively technical assistance, practiced at the is evolving from the evaluation ability, systems, effective use of resources. focused resource relevant policies and regulations. regulations. regulations. developed and recognition performance plan school level. school-led initiatives. provision recognition Page of technical 2 and of 5 management system. guidelines in adjustment. conducting ability system; assistance, incentive system recognition is 4. Regular monitoring, Stakeholders are Stakeholders Stakeholders are regular review and updating of gaps are addressed through and being refinement practiced.of evaluation, and reporting invited to participate collaboratively engaged, able community initiatives. appropriate action. plans.
PART V. SCORING INSTRUCTIONS 1. The four (4) principles were assigned percentage weights on the basis of their relative importance to the aim of school (improved learning outcomes and school operations); Leadership and Governance - 30% Curriculum and Learning – 30% ability and Continuous Improvement – 25% Management of Resources – 15% 2. Each principle has several indicators. Based on the results of the D-O-D (Document Analysis, Observation, Discussion),summarize the evidences, and arrive at a consensus, what rating to give to each indicator; 3. Rate the items by checking the appropriate boxes. These are the points earned by the school for the specific indicator. The rating scale is: 0 - No evidence 1 - Evidence indicates early or preliminary stages of implementation 2 - Evidence indicates planned practices and procedures are fully implemented 3 - Evidence indicates practices and procedure satisfy quality standards 4. Assemble the Rubrics rated by the respondents; edit them for errors like double entries or incomplete responses; 5. Count the number of check marks in each indicator and record in the appropriate box in the summary table for the area / standard rated; 6. Multiply the number of check marks in each column by the points (1-3); 7. Get the average rating for each principle by dividing the total score by the number of indicators of the principle; Page 3 of 5
8. Record the average ratings for the principle in the Summary Table for the computation of the General Average; 9. Multiply the rating for each principle by its percentage weight to get the weighted average rating; 10.
To get the total rating for the four principles, get the sum of all the weighted ratings. The value derived is
the school rating based on DOD;
11.The level of practice will be computed based on the criteria below: 60% based on improvement of learning outcomes; – 10% increment: 25 points – 20% increment: 50 points – 50% increment: 100 points 40% according to the validated practices using DOD – 0.00 - 0.50: 25 points – 0.51 – 1.50: 50 points – 1.51 – 2.50: 75 points – 2.51 – 3.00: 100 points 12.
The resulting score will be interpreted as: Level III: 150-200 points Level II: 149-100 points Level I: 99 and below
PART VI. DESCRIPTION OF SBM LEVEL OF PRACTICE The resulting levels are described as follows: Page 4 of 5
Level I: BEGINNING -Establishing and developing structures and mechanisms with acceptable level and extent of community participation and impact on learning outcomes. Level II: DEVELOPING - Introducing and sustaining continuous improvement process that integrates wider community participation and improve significantly performance and learning outcomes. Level III: ADVANCED (ACCREDITED) - Ensuring the production of intended outputs/outcomes and meeting all standards of a system fully integrated in the local community and is selfrenewing and self-sustaining.
Page 5 of 5
Part I: Introduction The Revised School-Based Management (SBM) Assessment tool is guided by the four principles of ACCESs (A Childand Community- Centered Education System). The indicators of SBM practice were contextualized from the ideals of an ACCESs school system. The unit of analysis is the school system, which may be classified as beginning, developing or advanced (accredited level). The SBM practice is ascertained by the existence of structured mechanisms, processes and practices in all indicators. A team of practitioners and experts from the district, division, region and central office validates the self-study/assessment before a level of SBM practice is established. The highest level- “advanced” is a candidacy for accreditation after a team of external validators confirmed the evidence of practices and procedures that satisfies quality standards. Part II: Basic School/Learning Center (LC) Information: School/Learning Center: Region/Division: Name of School Head/LC Head: Address: Part III: Instruction to the s: Please indicate using a check mark the extent of SBM practice for each indicator listed below (numbered) based on the validation team’s consensual agreements after systematic D-O-D (Document Analysis-Observation-Discussion). For indicators with no evidence, indicate zero. Part IV: Rating Scale: 0 No evidence 1 Evidence indicates beginning structures and mechanisms are in place to demonstrate ACCESs 2 Evidence indicates planned practices and procedures are fully implemented and aligned to ACCESs 3 Evidence indicates practices and procedure satisfy quality standards Page 1 of 5
D. Management of Resources 1 2 3 8. Learners are equipped with Learners Learners Learners Resources are collectively A. Leadership and essential knowledge, skills, accomplish demonstrate demonstratehigh level and judiciously mobilized and Governance and values to assume minimum progressive of attainment of managed with transparency, A network of that system 3. leadership The ability Community Community A communityresponsibility and proficiency levels in improvements desired competencies effectiveness, and efficiency. provides the vision and that is owned for by their the own stakeholders are stakeholders accepted ability all aspects ofare the beyondinventory the minimum and life skills. Regular resource Stakeholders Resource Resource inventories direction to 1. the education community is invited to participate contribute to the of ability system learning. desired level of attainment is aware that a regular ischaracterized by are systemically system makinginventory it relevant continuously enhanced in setting up an development of an effects continuous competencies. competencies. collaboratively resource inventory is regularity, increased developed and and responsive to the to ensure that ability ability system improvement in the undertaken by learning available and is used participation by stakeholders are contexts C. of diverse management structures system for schoolcoversboth schoolmanagement of ability and managers, learning as the basis for stakeholders, and engaged in a communities. and mechanisms are based management based learning. Continuous Improvement facilitators, and community resource allocation communicated to the collaborative process 1. There isAinclear, place a mechanism In place is a The VMG is used The mechanism responsive transparent, to the emerging processes, andcommunity-wide stakeholders as basis for mechanism and mobilization. community that allows for the that collaboratively by as the empowers to themake decisions on inclusive, learning andresponsive needs and structures and managementof resource allocation andallows for the allocation development of a shared the schoolbasis and for resourcecommunityresource to lead not ability demands of system the community. is in mechanisms. education. mobilization. allocation vision,place, mission, and development of VMG community as guide and only in the and mobilization. collaboratively mobilization. goals(VMG) which by reflects by the school programs. aredevelopment of the 4. ability assessment Theand school, with in initiating Stakeholders Stakeholders developed community 2. There is a regular Stakeholders are Stakeholders Stakeholders the aspirations and thrusts of monitors communitytheparticipation . criteria and tools, of engaged in the VMG but incontinuously and stakeholders, which dialogue for planning invited to participate regularly engaged in collaborate to ensure the community. mechanisms, and stakeholders, development andmakingprograms collaboratively review expected and actual and resource in the development the planning andguided by community timely and need-based information collection and articulates an operation of an and enhance performance, continually programming, that is of educational plan resource and resource aspirationsplanning and thrusts. validation ability appropriate ability addresses the techniques gaps, and and accessible and inclusive, with resource programming and programming and processes arefor inclusive assessment ability systems’ processes, ensures a venue to continuously engageThe school, programming andThe schoolactively participate inschool 2. The organization’s vision, vision, vision, The vision, continuous and collaboratively framework with basic assessment system. mechanisms and and redress. stakeholders and direction, participate in the the and implementation of implementation of the direction, and aspirations are and direction, direction and 1. developed Roles and responsibilities and agreed of There components, is an active The stakeholders are Shared tools.and participatory implementation of aspirationsimplementation. the education plan. education plan. periodically the revisited and are in aspirations are aspirations are able upon. (PROCESS) person/s and party including that initiates engaged in clarifying processes of education place but there’s no adjusted by community the learning reviewed and reviewed regularly to collective body/ies are clarification implementation of the and defining their determiningroles, plans. facilitators, managers, learning plan yet on how to adjusted sometimes adjust and make them clearly definedand roles guidelines. specific roles and responsibilities, and and community stakeholders keep them responsive to respond to responsive to 5. Participatory School initiated Collaborative conduct School-communityagreed upon by andresponsibilities in responsibilities. abilities of is in place a Stakeholders Stakeholders areconditions and Stakeholders sustain to respond3.toThere the community’s to changes in the conditions and assessment of periodic performance of performance developed community stakeholders. educationdelivery. stakeholders in community-developed judicious, share the implementation conditions and emerging emerging engaged needs. andinforms emerging performance needs. performance is done environment. assessments which assessment managing resource management appropriate, and expertise in the and improvement of a needs. regularly with the involve participation planning, plan assessment is anding system that drives effective use of Dialogues and collaborative collaboratively 3. Stakeholders actively Dialogues and Dialogues and community. Assessment of stakeholders. adjustments and practiced and is the education. appropriate behaviors consensus of resources. development of consensus developed, participate, through are seldom consensus are often are always 2. A results chievement and lessons of goals learned is Performance A community-level requirements for basis A communityfor improving the stakeholders to ensure resource periodically adjusted, dialogue and/or consensusused in formulating used in formulating used in formulating recognized serve as basis based for , on a ability is ability technical assistance. system monitoring accepted performance and judicious, appropriate, school and policies and management system. and and constituent building, in formulating school policies and school policies collaboratively technical assistance, practiced at the is evolving from the evaluation ability, systems, effective use of resources. focused resource relevant policies and regulations. regulations. regulations. developed and recognition performance plan school level. school-led initiatives. provision recognition Page of technical 2 and of 5 management system. guidelines in adjustment. conducting ability system; assistance, incentive system recognition is 4. Regular monitoring, Stakeholders are Stakeholders Stakeholders are regular review and updating of gaps are addressed through and being refinement practiced.of evaluation, and reporting invited to participate collaboratively engaged, able community initiatives. appropriate action. plans.
PART V. SCORING INSTRUCTIONS 1. The four (4) principles were assigned percentage weights on the basis of their relative importance to the aim of school (improved learning outcomes and school operations); Leadership and Governance - 30% Curriculum and Learning – 30% ability and Continuous Improvement – 25% Management of Resources – 15% 2. Each principle has several indicators. Based on the results of the D-O-D (Document Analysis, Observation, Discussion),summarize the evidences, and arrive at a consensus, what rating to give to each indicator; 3. Rate the items by checking the appropriate boxes. These are the points earned by the school for the specific indicator. The rating scale is: 0 - No evidence 1 - Evidence indicates early or preliminary stages of implementation 2 - Evidence indicates planned practices and procedures are fully implemented 3 - Evidence indicates practices and procedure satisfy quality standards 4. Assemble the Rubrics rated by the respondents; edit them for errors like double entries or incomplete responses; 5. Count the number of check marks in each indicator and record in the appropriate box in the summary table for the area / standard rated; 6. Multiply the number of check marks in each column by the points (1-3); 7. Get the average rating for each principle by dividing the total score by the number of indicators of the principle; Page 3 of 5
8. Record the average ratings for the principle in the Summary Table for the computation of the General Average; 9. Multiply the rating for each principle by its percentage weight to get the weighted average rating; 10.
To get the total rating for the four principles, get the sum of all the weighted ratings. The value derived is
the school rating based on DOD;
11.The level of practice will be computed based on the criteria below: 60% based on improvement of learning outcomes; – 10% increment: 25 points – 20% increment: 50 points – 50% increment: 100 points 40% according to the validated practices using DOD – 0.00 - 0.50: 25 points – 0.51 – 1.50: 50 points – 1.51 – 2.50: 75 points – 2.51 – 3.00: 100 points 12.
The resulting score will be interpreted as: Level III: 150-200 points Level II: 149-100 points Level I: 99 and below
PART VI. DESCRIPTION OF SBM LEVEL OF PRACTICE The resulting levels are described as follows: Page 4 of 5
Level I: BEGINNING -Establishing and developing structures and mechanisms with acceptable level and extent of community participation and impact on learning outcomes. Level II: DEVELOPING - Introducing and sustaining continuous improvement process that integrates wider community participation and improve significantly performance and learning outcomes. Level III: ADVANCED (ACCREDITED) - Ensuring the production of intended outputs/outcomes and meeting all standards of a system fully integrated in the local community and is selfrenewing and self-sustaining.
Page 5 of 5